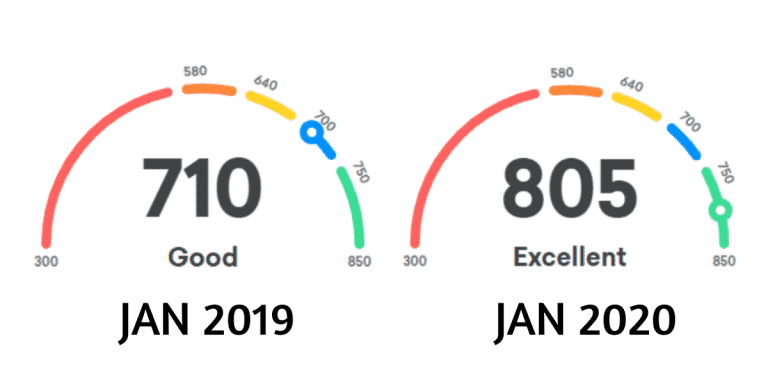
7 Ways to Improve Your Credit Score
From Average to Excellent: 7 Ways to Enhance Your Credit Score
Your credit score is one of the most important measures of your financial health. It tells the lenders how you use your credit. If your score is better, it is easier to gain approval for any new loans or lines of credit.
A higher credit score will have the lowest available interest rates when a sum is borrowed. If you want to improve your credit score, there are a few simple things you should do. It takes some time and effort to improve your credit score, but it’s worth it.
Here is a step-by-step guide for achieving a better credit score.
Review Your Credit Reports
To improve your credit score, checking your credit reports plays a major part. This helps to know what might be working in favor or against you.
Get your credit report from each of the three credit bureaus (Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion). You can get a free credit report once a year. Then review each report to see what is helping or hurting your score.
Late or missed payments, high credit card balances, collections, and judgments are major credit score detractors.
These are factors that affect your credit score:
- On-time payments
- Low balances on credit cards
- A mix of different credit cards
- A mix of different loan accounts
- Older credit accounts
- Minimal inquiries for new credit
Handling your Bills
Your payment history is another important factor in determining your credit score. If you have a long history of on-time payments, then you’ll have an excellent credit score.
You should not miss your loan or credit card payments by the assured date. If your payments are late by 30 days, then report them to the credit bureaus, so that your credit scores don’t get hurt.
Many lenders use FICO credit scores which are determined by the following factors:
- Payment history
- Credit usage
- Age of credit accounts
- Credit mix
- New credit inquiries
Credit Utilization Ratio
The credit utilization ratio refers to the part of the credit limit that you’re using at any given time. After payment history, it’s an important factor for FICO credit score calculations.
To keep your credit utilization ratio in check is to clear your credit card balances every month. If you’re unable to clear your balance, then keep the outstanding balance at 30% or less of your credit limit.
Requests for New Credit and Hard Inquiries
The credit history includes two types of inquiries. They are
A soft inquiry generally involves you checking your credit. Soft inquiries will not affect your credit score.
Hard inquiries can affect your credit score for a few months to two years. Hard inquiries include applications for a new credit card, a mortgage loan, an auto loan, or some other new credit. Many hard inquiries in a short period can damage your credit score.
If you’re trying to improve your credit score, then avoid applying for new credit for a while.
Pay Down Revolving Account Balances
If you’re having a high balance on revolving credit accounts, it can lead to a high credit utilization rate and hurt your credit scores.
Revolving accounts include credit cards and lines of credit, and maintaining a low balance on them. Maintaining a low balance on revolving accounts relative to their credit limit can help to improve your credit score.
Do not Remove Old Accounts from the Report
Some people remove old or deactivated accounts or accounts with negative history from their credit reports. They even try to remove their old debts from their reports once they pay them. Negative histories are bad for the score, but they are removed from the credit report after some time.
Getting old accounts removed may harm your score a lot as it may have a good repayment history. If you have paid your debts, then make sure you keep them in your report. It will improve your score and also show your creditworthiness.
Credit Monitoring Service
A credit monitoring service is an easy way to see how your credit score changes over time. These services check for changes in your credit report, such as a paid-off account or a new account that you’ve opened. They give access to any one of your credit scores from the credit bureaus.
How Long Does It Take to Rebuild a Credit Score?
There is no definite timeline for rebuilding your credit. Time taken to improve your credit score depends on what’s hurting your credit and the steps you’re taking to rebuild it.
If your score is low after a single missed payment, then it might not take too long to rebuild your account. If you miss payments on many accounts and you fall over 90 days behind before catching up, it will likely take longer to recover. This effect can be more inflated if your late payments result in repossession.
Credit bureaus have 30 days to investigate the error. If they agree that it is an error, they will remove the item. The credit bureau will ask for some additional information from the creditor involved. In that case, top communications with your creditors can get things resolved as soon as possible.
Suggested Reading:
- The Benefits of Having A High Credit Score
- How to Increase Credit Score (FAST with Timelines)
- 600 Credit Score – Is This A Good Credit Score?
Key Takeaway
Improving your credit score is a necessary goal if you’re planning to apply for a loan to make a major purchase, like a new car or home.
It can take several weeks, and sometimes several months to see a noticeable impact on your credit score.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can you make your credit score improve quickly?
By paying down your credit card debts, increasing your credit limit, checking your credit reports frequently for errors, and notifying creditors.
How often do credit scores change?
Your credit score changes as your credit report changes. It can change when some new information is added to your credit reports; this can be you applying for a job, you get a loan, or you get a new credit card.
What are score factors?
Score factors are codes provided with a credit score. They describe how items in your credit report influence the score. These factors identify which items have the greatest impact.