






By clicking ‘Get Started’ I agree by electronic signature to: (1) be contacted by The Credit Pros by a live agent, artificial or prerecorded voice, and SMS text at my residential or cellular number, dialed manually or by autodialer even if my phone number is on a do-not-call registry (consent to be contacted is not a condition to purchase services); and (2) the Privacy Policy and Terms of Use.







The Credit Pros has been helping people like you repair their credit score by updating or removing inaccurate items (especially debt collection brands) on credit reports for over a decade.
Our commitment is to making sure that everyone has a fair shot at good credit. Founded by a team of credit law experts, The Credit Pros wants to make sure that everyone has access to the same information and can learn what it takes to build good credit for a lifetime.
Not only do we offer credit repair and improvement services, we also provide financial and credit building tools and education resources to help our clients understand what’s on their report (e.g. like specific negative items, etc.) and how their credit score works. With this education and our AI-based credit management tools, our clients can work to take control of their financial future and live a life without credit worries.
Your credit score determines how much you pay to borrow money to cover modern day essentials including housing, cars, credit cards and loan interest rates.
Use the slider below to see how your credit score range impacts how much you pay for the same items over time. Then ask yourself, can you afford NOT to fix your credit?

Home Loan

Car Loan

Loan

Credit card
Loan Type
30 Year Fixed Mortgage
60 Month New Auto
Personal Loan (2yrs)
Revolving Credit
Loan Amount
APR
Monthly Payment
Total Interest
The Credit Pros offers affordable plans to help you increase your credit score so you pay less for the essentials (and the extras) in life.
Easy-to-read credit reports and personalized score insights
Tools & tips to help you understand your score and take the next step.
Credit Monitoring is Included at No Additional Charge which can help you spot potential identity theft.







A credit report contains information about an individual’s credit history and financial background. Your credit report will include your full name, any aliases, current and previous addresses, date of birth, Social Security number, phone numbers, and employment.
It will list all types of credit accounts, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages. Also included are public records (such as tax liens, legal judgements, bankruptcy and foreclosures), credit inquiries from credit applications and soft inquiries for pre-approved offers, and accounts sent to collections for overdue debts.
Credit reports do not include checking or savings account details, income, investments, or criminal records. Credit reports are essential for lenders and others assessing creditworthiness and are used to calculate credit scores.
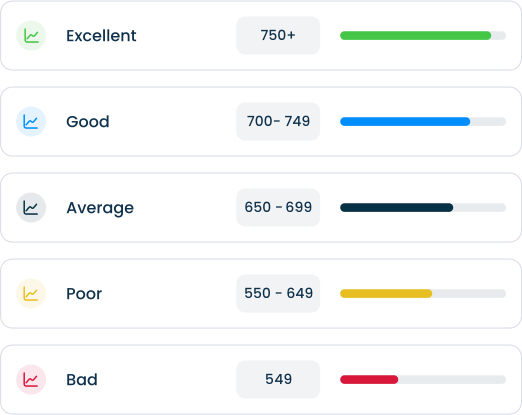
Your credit score is a 3-digit number between 300 and 850 that shows how creditworthy you are. Lenders use your credit score to decide whether or not you qualify for loans. They also use your credit score to determine your interest rate.
Credit scores are calculated using a 5-part formula, calculated based on the following factors: payment history, amounts owed, length of credit history, mix of types of credit, and amount of new credit.

Good credit is crucial for family members living in the same household as it directly influences financial opportunities and stability for everyone involved.
Enrolling a partner or spouse in a credit-building program while building your own credit can be beneficial for several reasons. First, having strong credit scores for both partners is crucial when applying for joint financial products like mortgages or car loans, as lenders often consider the lower credit score to determine eligibility and interest rates. This means that even if one partner has an excellent credit score, a lower score from the other can result in less favorable loan terms.
When you join The Credit Pros, you will have the option to enroll a ‘family member’ for free ($0 enrollment fee) and get 50% off their monthly plan rate!
It only takes 90 seconds to sign up. Start fixing errors on your credit report and get help to increase your credit score. Your information is safe with us. We treat your data as if it were our own.
Privacy and Cookies
We use cookies on our website. Your interactions and personal data may be collected on our websites by us and our partners in accordance with our Privacy Policy and Terms & Conditions